-
Timing
Mon - Sat : 9:00 AM – 4:00 PM Sunday : Closed -
For Book Appointment
+91 97002-85555 +91 90526-77688
Navigating Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Guide
- Home
- Navigating Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Guide
- Sanjeevani Hospital
- Mar 18, 2023
Introduction
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is a temporary form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and affects the way your body processes sugar. While it usually resolves after childbirth, it requires careful management to ensure the health of both the mother and the developing baby. In this article, we'll explore the nuances of GDM, its risk factors, effects, and strategies for managing it to ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
Understanding Gestational Diabetes:
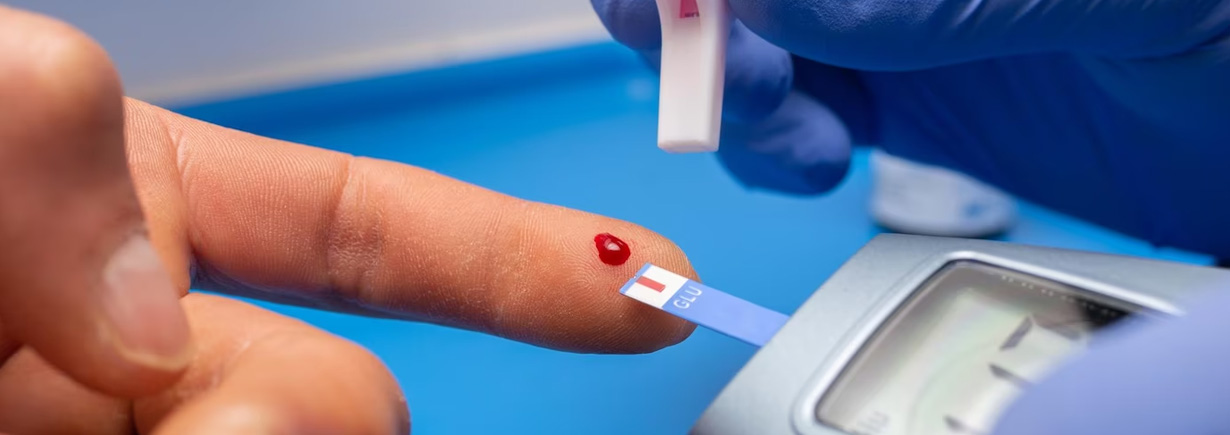
GDM occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands during pregnancy. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which can pose risks to both the mother and the baby. Regular prenatal care, including glucose testing, is crucial to identify and manage GDM effectively.
Risk Factors and Causes:
Several factors increase the risk of developing GDM:
- - Obesity: Being overweight before pregnancy increases the likelihood of GDM.
- - Age: Women over 25, especially those over 35, are at a higher risk.
- - Family History: A family history of diabetes raises the risk.
- - Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups are more prone to GDM.
- - Previous GDM: A history of GDM in previous pregnancies increases the risk.
- - Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS have a higher risk.
Effects and Complications:
Uncontrolled GDM can lead to several complications for both the mother and the baby:
- - Mother: Increased risk of high blood pressure, preeclampsia, and Type 2 diabetes later in life.
- - Baby: Higher birth weight, which can lead to birth trauma, C-section delivery, and increased risk of childhood obesity.
Managing Gestational Diabetes:
- 1. Dietary Changes: Working with a registered dietitian to create a balanced meal plan that controls blood sugar levels.
- 2. Physical Activity: Engaging in regular, approved exercises to help regulate blood sugar.
- 3. Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly check blood sugar levels to ensure they stay within a healthy range.
- 4. Medication: Some women may require insulin or other medications if lifestyle changes are insufficient.
- 5. Prenatal Care: Regular medical check-ups and monitoring to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.
- 6. Birth Plan: Collaborating with healthcare providers to create a birth plan that considers the baby's health and potential complications.
Conclusion:
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus demands vigilance and care, as it can impact both the mother's and the baby's health. By adopting a proactive approach to managing blood sugar levels through proper nutrition, exercise, and medical guidance, women with GDM can navigate pregnancy with confidence. Regular prenatal care, communication with healthcare providers, and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle can pave the way for a successful pregnancy journey and the birth of a healthy baby.
Popular links
Contact us
- Address: 29-26-129, Jadagamvari St, Moghalrajpuram, Suryaraopeta, Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh - 520002
- Call: +91 97002-85555, +91 90526-77688
-
Our Timing:
Mon - Sat : 9:00 AM – 4:00 PM
Sunday : Closed
© 2026 - All Rights Reserved By Sanjeevani Hospital